
Recording transactions in T-accounts involves the meticulous placement of debits and credits to their respective sides, ensuring that each financial event is accurately captured and balanced. This dual-entry system is fundamental to maintaining the integrity of financial records. In double-entry bookkeeping, a widespread accounting method, all financial transactions are considered to affect at least two of a company’s accounts. One account will get a debit entry, while the second will get a credit entry to record each transaction that occurs. A T-account is a term used in accounting practices to refer to double-entry bookkeeping. This account is used to accurately illustrate the addition and subtraction of variables to the balances of accounts.

My bank account is credited £4000, whilst the accounts payable account is debited £2000 and rent is debited £2000. Therefore, both debits and credits are equal in this transaction. T-accounts serve as fundamental tools within the accounting discipline, providing a visual aid for understanding and recording financial transactions. They enable the simplification of complex accounting entries, facilitate the detection of discrepancies, and are instrumental in the educational process for aspiring accountants.
We’re going to look at T accounts but before that, let’s lay out some of the terminologies you might come Legal E-Billing across so you can grasp T accounts better. This visual guide helps you ensure figures are being posted in the correct way, potentially reducing data entry errors. The three components of a T-account are the title, debit side, and credit side.


In double-entry accounting, debits and credits always need to balance out. No, journal entries are recorded in the journal and later posted in the respective books of accounts, which are in the form of the T-accounts. Even coming from an accounting background, most individuals have no idea about the term “T-account.” This is because of the introduction of this term by https://www.bookstime.com/articles/what-are-t-accounts new accounting students in recent times. To understand it briefly, it is a ledger account that is used to record the rise and decline in the value of respective balances.
A balance sheet is a summary of a company’s financial position at a given point in time. The balance sheet summarizes the financial position of the company at the end of a specific period, usually at the end of the fiscal year. It is used by stakeholders to evaluate a company’s financial strength and to make investment decisions. To pay the rent, I’ve used cash, so my bank account (an asset account) is credited by £2000. I’ve agreed to pay for the coffee machine next month so my accounts payable is increased (credited) by £700.
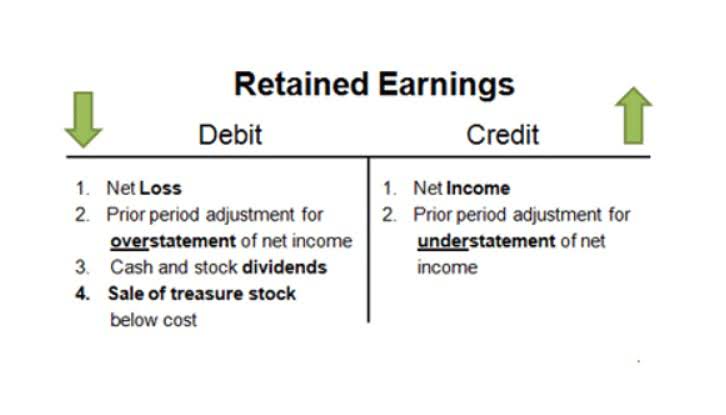
A T-Account is a visual presentation of the journal entries recorded in a general ledger account. This T format graphically depicts the debits on the left side of the T and the credits on the right side. This system allows accountants and bookkeepers to easily track account balances and spot errors in journal entries. A T-account, fundamental to the practice of double-entry bookkeeping, provides a visual structure for maintaining the balances of individual ledger accounts. Represented by a large letter T, this method allows accountants to track the financial transactions of a business with precision and clarity.

Finally, the difference between the two numbers is the balance on the T-Account. A T-account can have many different types of transactions within it but they must always follow this same basic format. The first transaction that involves the bank account occurs on the 1st of CARES Act April, where Mr. Burnham invested $15,000 in the business.







Partilhar.